
What is immersive technology?
Immersive technology is a term used to describe technologies that create a sense of immersion or presence, which is the feeling of being fully present in a digital or virtual environment. Immersive technology can include VR, AR, and MR, as well as other technologies that provide an interactive or enhanced experience of reality. Immersive technology is already being used in a wide range of applications, including gaming, healthcare, defense, education, and industrial training.
Let’s take a closer look at each term within immersive technology, and explore the context behind them.
What is Virtual Reality?
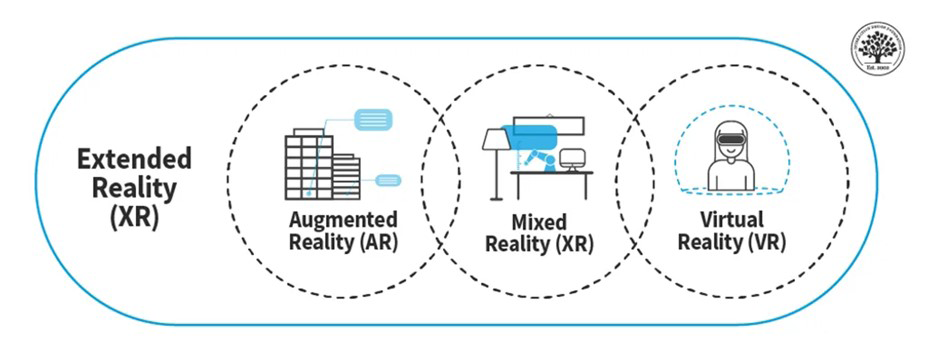
Virtual reality (VR) is a technology that immerses users in a completely simulated environment, typically involving the use of a headset or other device that replaces the real world and allows users to interact with a digital environment. Virtual reality headsets have applications from entertainment to enterprise, and are continuing to revolutionize sectors like aerospace, automotive, education, and healthcare.
A recent example of leading VR technology is the Meta Quest Pro, released in October of 2022. Other examples include the HTC Vive XR Elite, which was launched earlier this year. As we mentioned in our post on How to Launch an XR Product, the VR space is advanced, competitive, and often comes with a high barrier to entry in terms of research and development.
What is Augmented Reality?
Augmented reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital content onto the real world, typically through a smartphone or other mobile device. Unlike VR, augmented reality usually involves a blend of real-world stimuli and digitally-generated spaces and objects. AR has been used for gaming, e-commerce, advertising, and other industrial applications that rely on a mix of reality and digital information (see: Augmented Reality in Architecture, Engineering and Construction).
One of the most well-known examples of an AR app is Pokémon Go, released in 2016 by Niantic. The game was one of the first mainstream examples of augmented reality in action, with players using their smartphone as a viewfinder to catch Pokemon in the real world.
More recently, the Magic Leap 2 (released September 2022) is an example of headworn AR hardware. Marketed as ‘the most immersive enterprise AR device’, the Magic Leap 2 is a headset that overlays digital content onto the real world, allowing users to interact with virtual objects in a real-world environment. As a case in point, Audi recently used Magic Leap 2 to create a dynamic, merged reality interface for drivers, known as the Audi activesphere.
What is Mixed Reality?
Mixed reality (MR) is a type of immersive experience that blends the physical and digital worlds together to create a new type of environment where digital objects can interact with real-world objects, and vice versa. MR allows users to see and interact with virtual objects as if they were part of the real world, creating a seamless blend of the physical and digital realms. Unlike VR, which replaces the real world with a digital space, and AR, which overlays digital objects onto the real world, MR combines elements of both to create a hybrid environment where physical and digital objects coexist.
Importantly, AR and MR are often mistaken for one another at a qualitative level, since they both involve the interaction of digital objects in the real world. However, the distinction lies in how meaningful the user’s environment is as a staging ground for the digital content being projected onto it. In AR, digital objects are simply overlaid onto the user’s surroundings, which remain largely unchanged physically. In MR, however, real space and objects are modified (with the use of green screens, for example) connecting them in a meaningful way to the digital content that is being generated by a headset.
By way of example, mixed reality can be clearly seen in action in Varjo’s Pilot Training, a high-end immersive training solution that can help pilots train in a mixed reality environment. Varjo’s solution combines specific objects in the user’s surrounding environment (in this case, physical flight simulator controllers) with virtually-generated content, to create a more immersive training program for users.
What is Extended Reality?
Extended reality (XR) is an umbrella term that encompasses all immersive technologies, including VR, AR, and MR. XR refers to any experience that extends beyond the physical world through the use of digital technologies. It includes virtual environments that simulate real-world environments, augmented environments that overlay digital content onto the physical world, and mixed environments that blend both virtual and real-world elements. XR technologies are used in a wide range of applications, from entertainment and gaming, to education, healthcare, and industrial training.


